Welcome to Complete Care Physio's Patient Resource About Ankle Anatomy
The ankle joint acts like a hinge. But it’s much more than a simple hinge joint. Several important structures are making up the ankle anatomy. The unique design of the ankle makes it a very stable joint. This joint has to be stable in order to withstand 1.5 times your body weight when you walk and up to eight times your body weight when you run.
Normal ankle function is necessary in order to walk with a smooth and nearly effortless gait. The muscles, tendons, and ligaments that support the ankle joint work together to propel the body. Conditions that disturb the normal way the ankle works can make it difficult to do your activities without pain or problems.
This guide will help you understand the ankle anatomy:
- What parts make up the ankle
- How the ankle works
Important Structures
The important structures of the ankle anatomy can be split up into several categories. These include
- Bones and joints
- Ligaments and tendons
- Muscles
- Nerves
- Blood vessels
The top of the foot is referred to as the dorsal surface. The sole of the foot is the plantar surface.
Bones and Joints
Ankle Bones
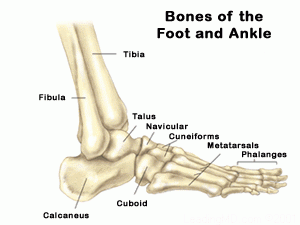
The connection of three bones is forming the ankle joint. The ankle bone is the talus. The top of the talus fits inside a socket that is put together by the lower end of the tibia (shinbone) and the fibula (the small bone of the lower leg). The bottom of the talus sits on the heel bone, called the calcaneus.
The talus works like a hinge inside the socket to allow your foot to move up (dorsiflexion) and down (plantarflexion).
Talus Works Like a Hinge
Woodworkers and craftsmen are familiar with the design of the ankle joint. They use similar construction, called a mortise and tenon, to create stable structures. They routinely use it to make strong and sturdy items, such as furniture and buildings.
Mortise and Tenon
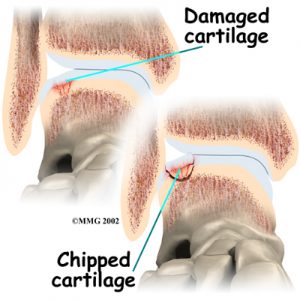
A slick material called articular cartilage is covering the bones inside the joint. Therefore, articular cartilage is the material that allows the bones to move smoothly against one another in the joints of the body.
Furthermore, the cartilage lining is about one-quarter of an inch thick in most joints that carry body weight, such as the ankle, hip, or knee. It is soft enough to allow for shock absorption but tough enough to last a lifetime, as long as it is not injured.
Cartilage
Ligaments and Tendons
Ankle
Ligaments are the soft tissues that attach bones to bones. They are very similar to tendons. The difference is that tendons attach muscles to bones. Both of these structures are made up of small fibers of a material called collagen. The collagen fibers are together to form a rope-like structure. Ligaments and tendons come in many different sizes and like rope, are made up of many smaller fibers. The thickness of the ligament or tendon determines its strength.
Collagen
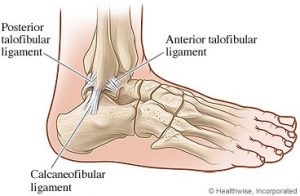
Ligaments on both sides of the ankle joint help hold the bones together. Three ligaments make up the lateral ligament complex on the side of the ankle farthest from the other ankle. (Lateral means further away from the center of the body.) These include the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL), the calcaneofibular ligament(CFL), and the posterior talofibular ligament (PTFL). A thick ligament, called the deltoid ligament, supports the medial ankle (the side closest to your other ankle).
Three Main Ligaments
Ligaments also support the lower end of the leg where it forms a hinge for the ankle. Also, this series of ligaments support the ankle syndesmosis, the part of the ankle where the bottom end of the fibula meets the tibia. Three main ligaments support this area. The ligament crossing just above the front of the ankle and connecting the tibia to the fibula is called the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL). The posterior fibular ligaments attach across the back of the tibia and fibula. These ligaments include the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (PITFL) and the transverse ligament. The interosseous ligament lies between the tibia and fibula. (Interosseous means between bones.) The interosseus ligament is a long sheet of connective tissue that connects the entire length of the tibia and fibula, from the knee to the ankle.
The ligaments that surround the ankle joint help form part of the joint capsule. A joint capsule is a watertight sac that forms around all joints. It is made up of the ligaments around the joint and the soft tissues between the ligaments that fill in the gaps and form the sac.
Joint Capsule
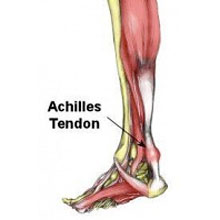
Nearby tendons are also supporting the ankle joint. The large Achilles tendon is the most important tendon for walking, running, and jumping. It attaches the calf muscles to the calcaneus (heel bone) and allows us to raise up on our toes. The posterior tibial tendon attaches one of the smaller muscles of the calf to the underside of the foot. This tendon helps support the arch and allows us to turn the foot inward.
Achilles Tendon
Posterior Tibial Tendon
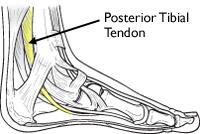
The anterior tibial tendon allows us to raise the foot. Two tendons run behind the outer bump of the ankle (the lateral malleolus). These two tendons, called the peroneals, help turn the foot down and out.
Muscles
Muscles of the Ankle
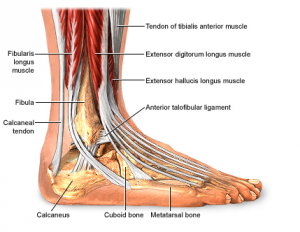
Stronger muscles in the lower leg are causing most of the motion, whose tendons pass by the ankle and connect in the foot. The contraction of the muscles in the leg is the main way that we move our ankles when we walk, run, and jump. The key ankle muscles have been discussed earlier in the section on ligaments and tendons. These muscles and their actions are also listed here.
- The peroneals (peroneus longus and peroneus brevis) on the outside edge of the ankle and foot bend the ankle down and out.
- The calf muscles (gastrocnemius and soleus) connect to the calcaneus by the Achilles tendon. When the calf muscles tighten, they bend the ankle down.
- The posterior tibialis muscle supports the arch and helps turn the foot inward.
- The anterior tibialis pulls the ankle upward.
Nerves
Nerves of the Ankle
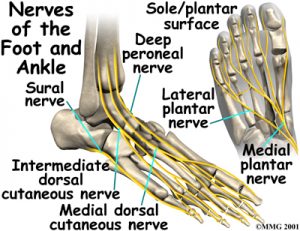
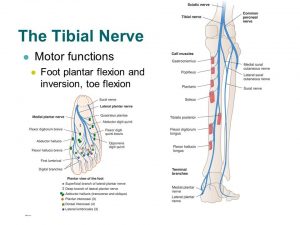
The nerve supply of the ankle is from nerves that pass by the ankle on their way into the foot. The tibial nerve runs behind the medial malleolus. Another nerve crosses in front of the ankle on its way to the top of the foot. There is also a nerve that passes along the outer edge of the ankle. The nerves on the front and outer edge of the ankle control the muscles in this area, and they give sensation to the top and outside edge of the foot.
Tibial Nerve
Nerves on Front and Outer Edge
Blood Vessels
The ankle gets blood from nearby arteries that pass by the ankle on their way to the foot. So the dorsalis pedis runs in front of the ankle to the top of the foot. (You can feel your pulse where this artery runs in the middle of the top of the foot.) In addition, another large artery, called the posterior tibial artery, runs behind the medial malleolus. It sends smaller blood vessels to the inside edge of the ankle joint. Other less important arteries entering the foot from other directions also supply blood to the ankle.
Posterior Tibial Artery
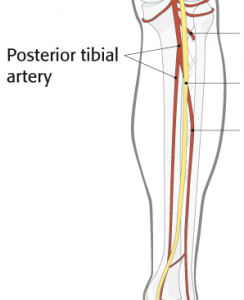
Arteries Entering the Foot
We have physiotherapy offices in Brampton, Mississauga, and Hamilton (Central Hamilton, Grimsby, Stoney Creek, Hamilton Mountain) who would be happy to receive you.
Summary
In conclusion, the anatomy of the ankle is very complex. When everything works together, the ankle functions correctly. When one part becomes damaged, it can affect every other part of the ankle and foot, leading to problems. If you are interested in our services we have physiotherapy offices in Brampton, Oakville, and Hamilton (East Hamilton, Stoney Creek, Hamilton Mountain) that would be happy to receive you.
Portions of this document copyright MMG, LLC.
